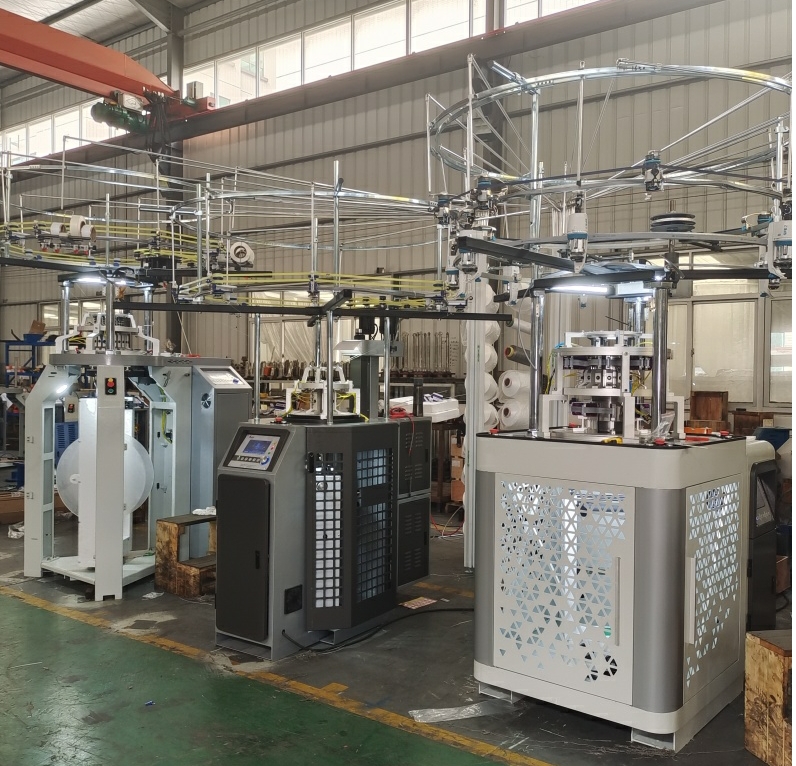
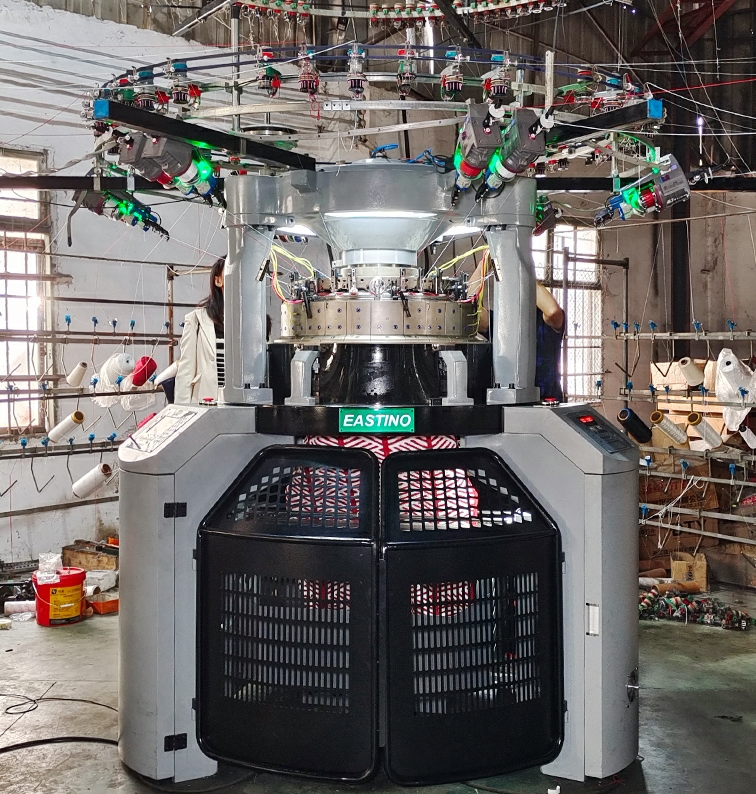
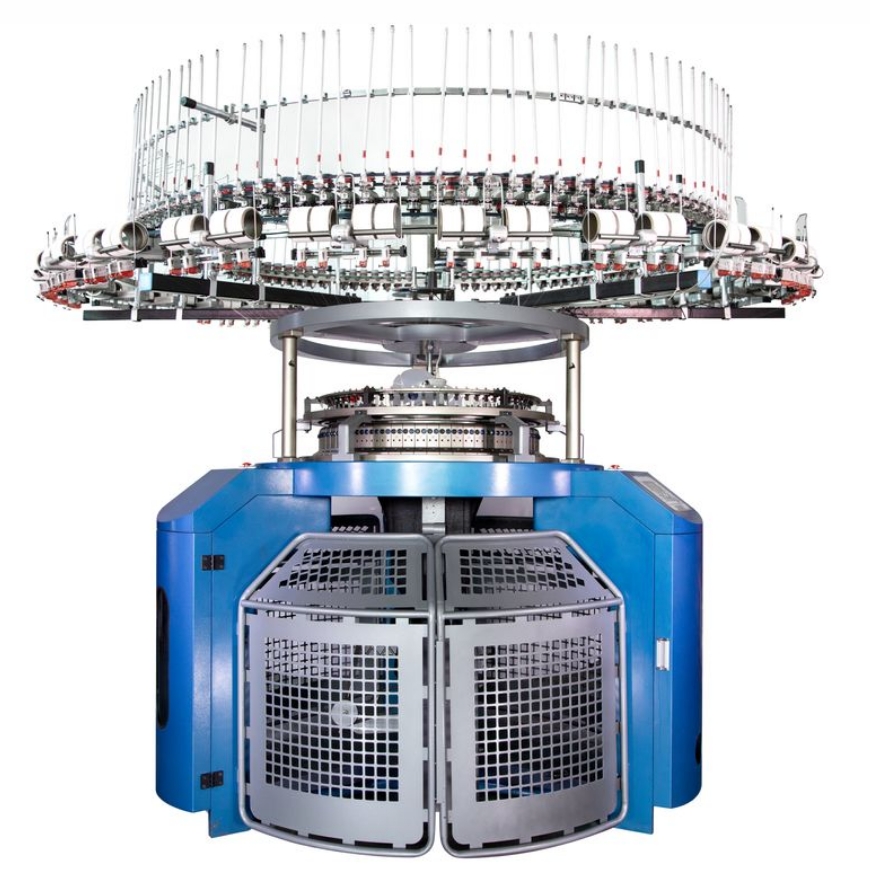
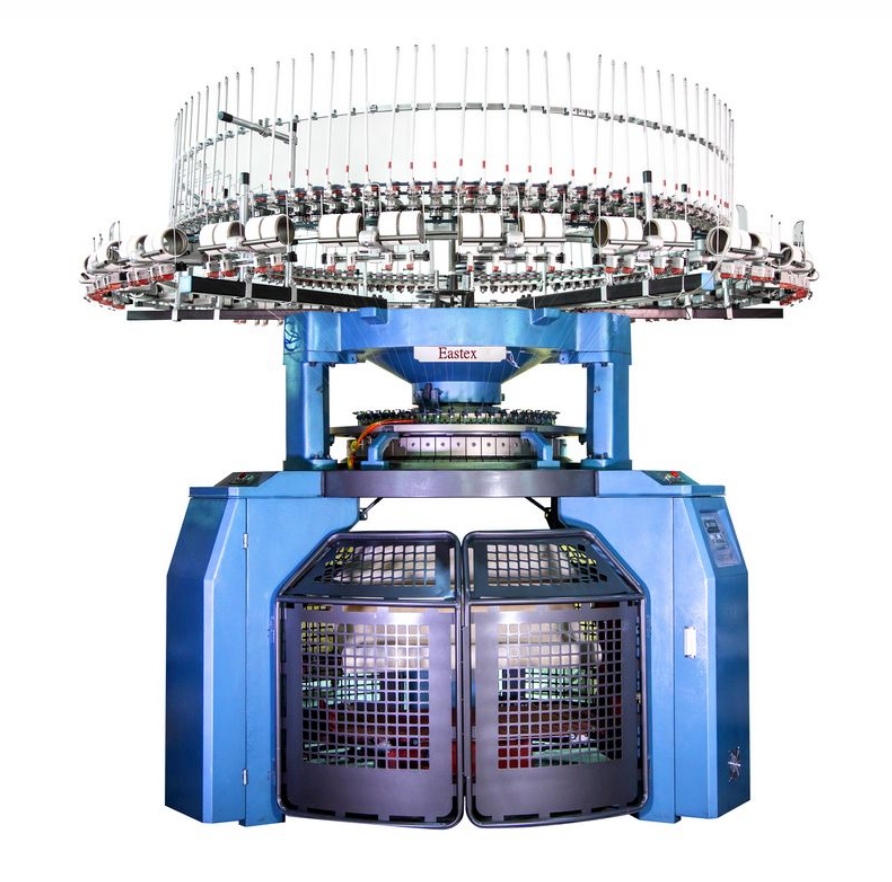
Production Process
The production process of Terry Fabric Circular Knitting Machines is a sophisticated sequence of steps designed to produce high-quality terry fabrics. These fabrics are characterized by their looped structures, which provide excellent absorbency and texture. Here’s a detailed look at the production process:
1. Material Preparation :
Yarn Selection : Choose high-quality yarns suitable for terry fabric production. Common choices include cotton, polyester, and other synthetic fibers.
Yarn Feeding : Load the yarn onto the creel system, ensuring proper tension and alignment to prevent breaks and ensure consistent feeding.
2. Machine Setup :
Needle Configuration : Set up the needles according to the desired fabric gauge and pattern. Terry knitting machines typically use latch needles.
Cylinder Adjustment : Adjust the cylinder to the correct diameter and ensure it is properly aligned with the sinker ring and cam systems.
Cam System Calibration : Calibrate the cam systems to control the movement of the needles and achieve the desired stitch pattern.
3. Knitting Process :
Yarn Feeding : The yarn is fed into the machine through the yarn feeders, which are controlled to maintain consistent tension.
Needle Operation : As the cylinder rotates, the needles form loops in the yarn, creating the fabric. The sinkers assist in holding and releasing the loops.
Loop Formation : Special sinkers or crochet needles elongate the sinker arc of the loop yarn to form the loops.
4. Quality Control :
Real-time Monitoring : Modern machines are equipped with advanced monitoring systems that track fabric density, elasticity, smoothness, and thickness in real-time.
Automatic Adjustments : The machine can automatically adjust parameters to maintain consistent fabric quality.
5. Post-processing :
Fabric Take-down : The knitted fabric is collected and wound onto a batch roller. The take-down system ensures the fabric is wound evenly.
Inspection and Packaging : The finished fabric is inspected for defects and then packaged for shipment.
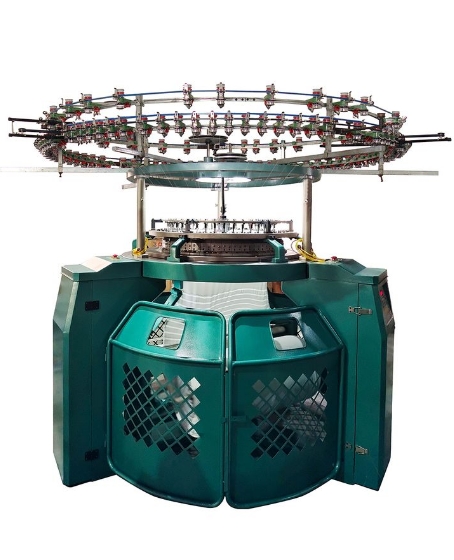
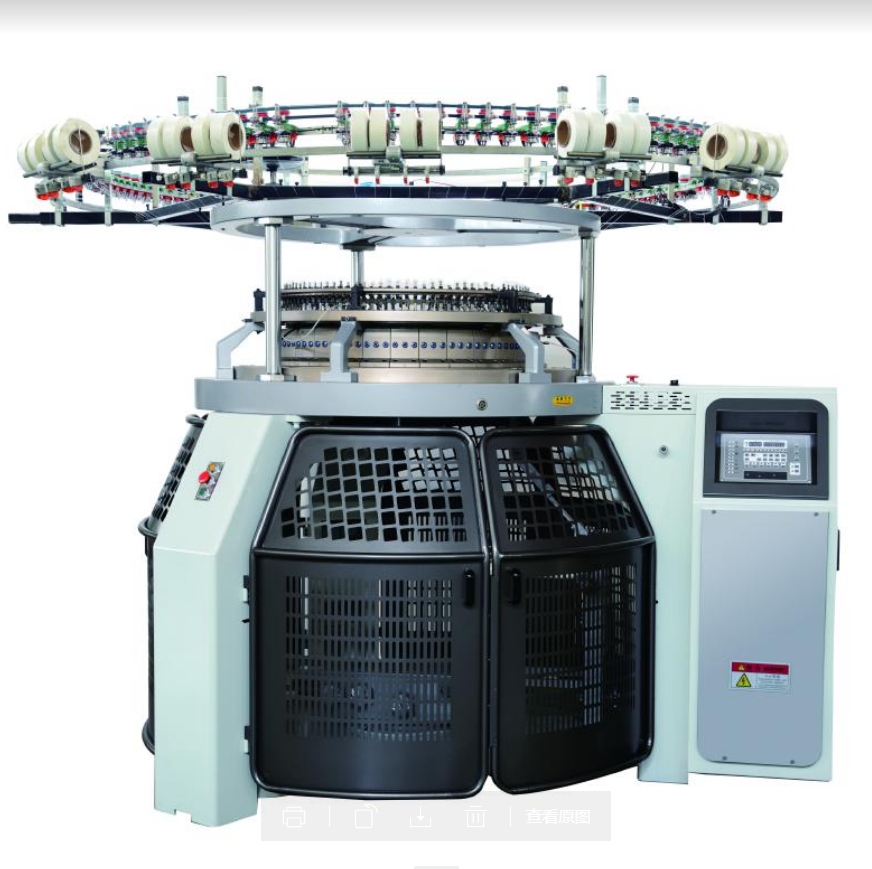
Components and Their Functions
1. Needle Bed :
Cylinder and Dial : The cylinder holds the lower half of the needles, while the dial holds the upper half.
Needles : Latch needles are commonly used for their simple action and ability to process various types of yarns.
2. Yarn Feeders :
Yarn Supply : These feeders supply yarn to the needles. They are designed to work with a variety of yarns, from fine to bulky.
3. Cam System :
Stitch Pattern Control : The cam system controls the movement of the needles and determines the stitch pattern.
4. Sinker System :
Loop Holding : The sinkers hold the loops in place as the needles move up and down, working in conjunction with the needles to create the desired stitch pattern.
5. Fabric Take-up Roller :
Fabric Collection : This roller pulls the finished fabric away from the needle bed and winds it onto a roller or spindle.
Configuration
Terry Fabric Circular Knitting Machines come in various configurations to meet different production needs. Key configurations include:
- Single Needle Bed Multi-cam Type : This type is widely used for its versatility and ability to produce different loop lengths.
- Double Needle Bed Circular Weft Machine : This model uses two needle beds to create loops of different lengths.
Installation and Commissioning
1. Initial Setup :
Machine Placement : Ensure the machine is placed on a stable and level surface.
Power and Yarn Supply : Connect the machine to the power source and set up the yarn supply system.
2. Calibration :
Needle and Sinker Alignment : Adjust the needles and sinkers to ensure proper alignment.
Yarn Tension : Calibrate the yarn feeders to maintain consistent tension.
3. Test Runs :
Sample Production : Run the machine with test yarns to produce sample fabrics. Inspect the samples for stitch consistency and fabric quality.
Adjustments : Make any necessary adjustments based on the test results to ensure optimal performance.
Maintenance and After-Sales Service
1. Regular Maintenance :
Daily Cleaning : Clean the machine surface and yarn creel to remove debris and fibers.
Weekly Inspections : Check the yarn feeding devices and replace any worn parts.
Monthly Cleaning : Thoroughly clean the dial and cylinder, including needles and sinkers.
2. Technical Support :
24/7 Support : Many manufacturers offer round-the-clock technical support to assist with any issues.
Warranty and Repairs : Comprehensive warranty coverage and fast repair services are available to minimize downtime.
3. Training :
Operator Training : Comprehensive training for operators on machine operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting is often provided.
4. Quality Assurance :
Final Inspection : Each machine undergoes a final inspection, cleaning, and packing before shipment.
CE Marking : Machines are often CE marked to ensure they meet high standards of safety and performance.
Conclusion
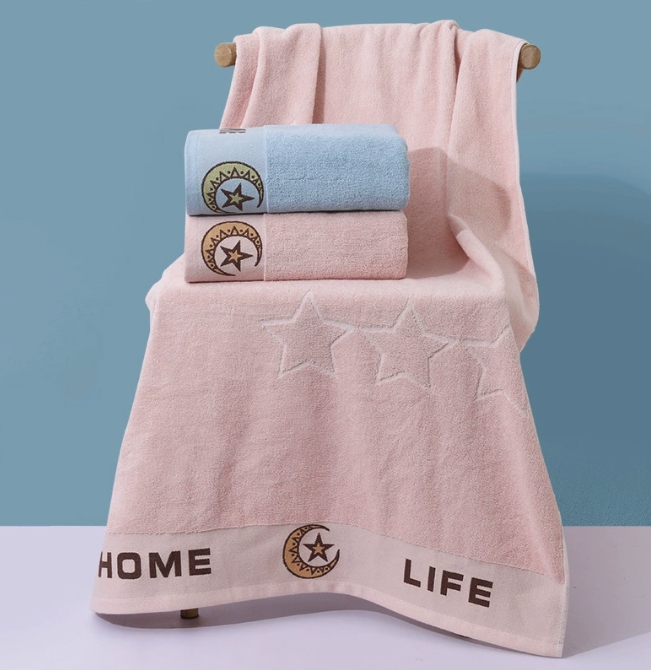
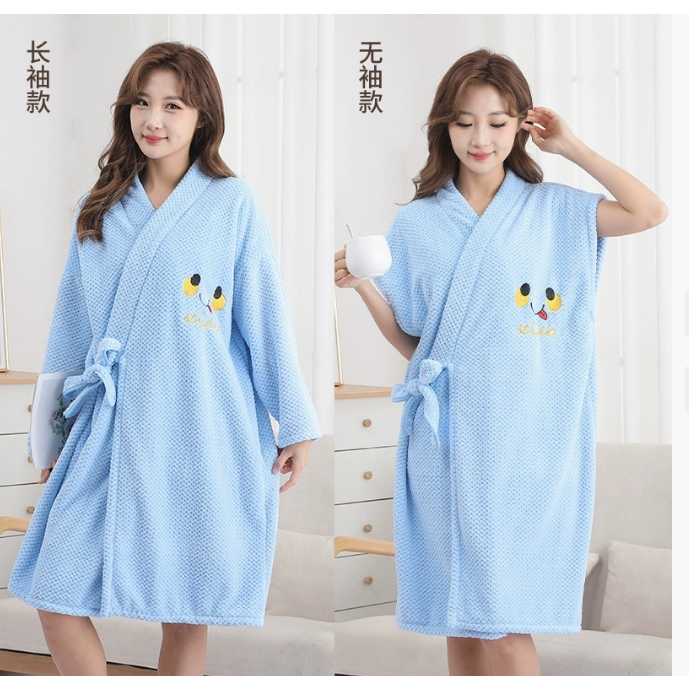
Terry Fabric Circular Knitting Machines are essential tools in the textile industry, capable of producing high-quality terry fabrics for various applications. The production process involves careful material preparation, precise machine setup, continuous knitting, quality control, and post-processing. These machines are highly versatile and find applications in apparel, home textiles, and technical textiles. By understanding the production process, components, configuration, installation, maintenance, and after-sales service, manufacturers can optimize their operations and meet the diverse needs of the textile market.
Post time: Apr-15-2025